The Medicare Trust Fund is an essential source of funding for healthcare services in the United States. As the population ages and healthcare costs continue to rise, the solvency of the trust fund has become a critical concern. In this article, we will explore the background, financial status, impact on beneficiaries, and comparison with the Social Security Trust Fund of the Medicare Trust Fund. The Medicare Trust Fund plays a crucial role in providing healthcare services to elderly and disabled individuals in the United States. It is the primary source of funding for the Medicare program and covers essential services such as hospital insurance, skilled nursing facility care, and home health care. Without the Medicare Trust Fund, millions of Americans would be without access to necessary healthcare services. For Your Copy of The Annual Report Click Here
Trustees’ Projection of Three-Year Gain
According to the latest Trustees’ report, the Medicare Trust Fund is projected to remain solvent for the next three years. However, the long-term financial stability of the trust fund remains a significant concern due to rising healthcare costs and an aging population.
Background of Medicare Trust Fund
Creation of Medicare Trust Fund
The Medicare Trust Fund was created in 1965 as part of the Social Security Act. It was established to provide funding for the Medicare program, which was designed to provide health insurance coverage for individuals over the age of 65 and those with disabilities.
Sources of Funding
The Medicare Trust Fund is funded through a combination of payroll taxes, general revenue from the federal government, and premiums paid by beneficiaries. The payroll tax rate for Medicare is currently set at 2.9%, split evenly between employers and employees.
Expenses Covered by the Fund
The Medicare Trust Fund covers a range of essential healthcare services, including hospital insurance (Part A), medical insurance (Part B), and prescription drug coverage (Part D). These services are crucial for ensuring that beneficiaries have access to the medical care they need to stay healthy and maintain their quality of life.
Financial Status of Medicare Trust Fund
Trustees’ Report on Solvency
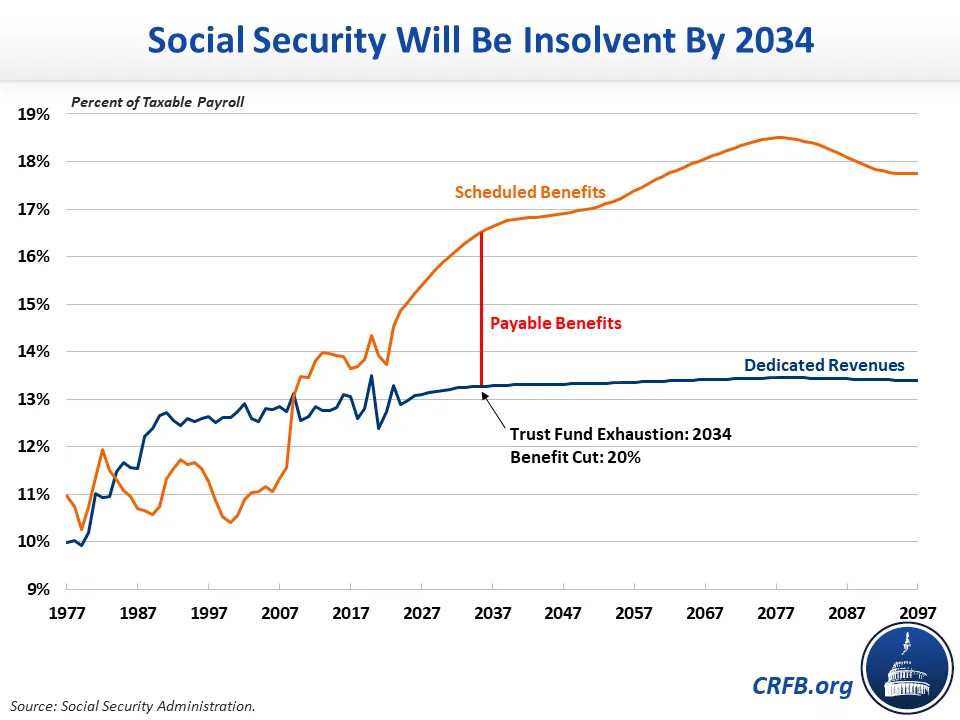
The Trustees’ report on the financial status of the Medicare Trust Fund is released annually and provides a projection of the trust fund’s solvency. According to the latest report, the trust fund is projected to remain solvent until 2026, after which it will be able to pay only 91% of its expenses.
Projected Growth in the Next Three Years
Despite the projected decline in solvency, the Trustees’ report also predicts that the Medicare Trust Fund will experience a net increase of $203 billion over the next three years. This increase is due to several factors, including lower projected healthcare spending and higher payroll tax revenue.
Factors Affecting the Trust Fund’s Solvency
The financial stability of the Medicare Trust Fund is affected by several factors, including the cost of healthcare services, the size and age of the beneficiary population, and the funding sources for the trust fund. As healthcare costs continue to rise, the Medicare Trust Fund’s solvency will become increasingly challenging to maintain.
Impact of Medicare Trust Fund on Beneficiaries
Importance of Medicare Trust Fund for Beneficiaries
The Medicare Trust Fund is critical for ensuring that beneficiaries have access to necessary healthcare services. It provides coverage for essential services such as hospital stays, doctor visits, and prescription drugs. Without the trust fund, many beneficiaries would be unable to afford the medical care they need.
Possible Changes in Medicare Benefits if the Trust Fund Becomes Insolvent
If the Medicare Trust Fund becomes insolvent, it could lead to significant changes in the Medicare program. Beneficiaries may be required to pay higher premiums, deductibles, and coinsurance
Measures Being Taken to Ensure the Trust Fund’s Solvency
To ensure the long-term solvency of the Medicare Trust Fund, several measures have been proposed. These measures include reducing healthcare costs, increasing funding sources, and making changes to the Medicare program. For example, some proposals suggest raising the payroll tax rate or reducing benefits for higher-income beneficiaries.
Comparison with Social Security Trust Fund
Similarities and Differences between Medicare and Social Security Trust Funds
The Medicare and Social Security Trust Funds are both essential sources of funding for vital programs that provide financial support to millions of Americans. However, there are several key differences between the two funds. The Social Security Trust Fund primarily funds retirement benefits, whereas the Medicare Trust Fund provides healthcare benefits. Additionally, the funding sources for the two programs are different.
Importance of Both Funds for American Citizens
Both the Medicare and Social Security Trust Funds are crucial for ensuring the financial security of millions of Americans. They provide essential benefits that help support individuals and families during retirement and provide access to necessary healthcare services.
Future Challenges and Solutions for Both Funds
As the population continues to age and healthcare costs rise, both the Medicare and Social Security Trust Funds will face significant challenges. To ensure their long-term solvency, policymakers will need to consider a range of solutions, including increasing funding sources, reducing expenses, and making changes to the programs themselves.
Conclusion
The Medicare Trust Fund plays a critical role in providing healthcare services to millions of Americans. While the trust fund is projected to remain solvent for the next three years, it faces significant challenges in the long term. By taking action to reduce healthcare costs, increase funding sources, and make changes to the Medicare program, policymakers can help ensure the trust fund’s solvency and provide essential healthcare benefits to those who need them


