Introduction
Medicare, a cornerstone of the U.S. healthcare system, serves a vast segment of the American populace. By 2023, it encompasses over 65.7 million beneficiaries. Among the myriad components that render Medicare comprehensive and dynamic, the Medicare Status Indicators shine for their central role in determining reimbursements. Let’s deep-dive into the data.

Medicare At A Glance
- Total Beneficiaries (2023): 65,748,297
- This marks a growth rate of approximately 1.6% over the prior year.
- Source
- Percentage of U.S. Population:
- Medicare beneficiaries made up about 18.4% of the U.S. population as of 2021.
- This proportion has seen a consistent incline over the past decade, underscoring Medicare’s growing influence in American healthcare.
- Source

Understanding Medicare Status Indicators
- What are they?
- Status Indicators play a pivotal role in the Outpatient Prospective Payment System (OPPS), guiding the intricacies of reimbursement.
- Source
- Their Significance:
- They provide clarity on how specific services and procedures are compensated, ensuring a transparent and predictable billing mechanism.
The Role of Status Indicators in Medicare
Status Indicators are essential components within the Medicare landscape, particularly in the context of the Outpatient Prospective Payment System (OPPS). They provide clear guidance on payment classifications for distinct services and procedures, ensuring that reimbursements are appropriately allocated.
Understanding Status Indicators
- Status indicators are symbols assigned to each service or procedure under the HCPCS/CPT codes in the Medicare system.
- They play a crucial role in determining if Medicare will reimburse a service and, if so, the method of reimbursement.
- Their primary function lies in the OPPS, where they influence the payment amount for individual services.
- Essentially, they offer a description, highlight the purpose, and underscore their significance in Medicare reimbursement.
2023 OPPS Status Indicators Breakdown
- Major Indicators: Represent significant procedures, typically demanding more resources and time.
- Minor Indicators: These cover procedures less resource-intensive than their major counterparts.
- Bypass Indicators: Services that can sidestep the regular Consolidated Billing (CB) system.
- Status S and T: Both these indicators have specific roles within the OPPS, affecting payment classifications and processing nuances.
Medicare Enrollment: A Historical Perspective
Medicare, a cornerstone of the American healthcare landscape, has seen a dynamic evolution in its enrollment trends over the years. This section delves deep into the historical trajectory of Medicare’s growth, the tug of war between traditional Medicare and its Advantage counterpart, and the influx of new beneficiaries.
1. Evolution of Enrollment
- From its inception in 1966, Medicare’s growth has been phenomenal. As of March 2023, the enrollment numbers have swelled to a staggering 65,748,297.
- Since 2019, the Medicare program has added an impressive 5.1 million beneficiaries, marking a significant uptick in its growth trajectory.
- Source
2. Traditional Medicare vs. Medicare Advantage: The Enrollment Tug of War
- While Medicare as a whole has seen consistent growth, the real story lies in the shifting sands between traditional Medicare and Medicare Advantage (MA) plans.
- Medicare Advantage enrollment has grown by 2.1 percent between 2019 and 2023, with a record 2.7 million increase in a single year.
- Contrastingly, traditional Medicare has seen a decline, losing a sizable 1.3 million beneficiaries in both 2022 and 2023.
3. The New Entrants: A Look at New Enrollees
- 2022 saw Medicare’s total enrollment rise by 1 million beneficiaries, a 1.6% growth from the previous year.
- As of the current year, these enrollees represent approximately 18.4% of the U.S. population, showcasing the pervasive reach and trust in the Medicare program.
- Source
Medicare Enrollment: A Deep Dive
Medicare’s reach across the U.S. has expanded steadily over the years, with both traditional Medicare and Medicare Advantage seeing significant enrollment.
- Total Enrollees (2023): 65,748,297
- An increase of almost 100,000 from the previous report in September.
- Source
- Medicare Advantage Enrollees:
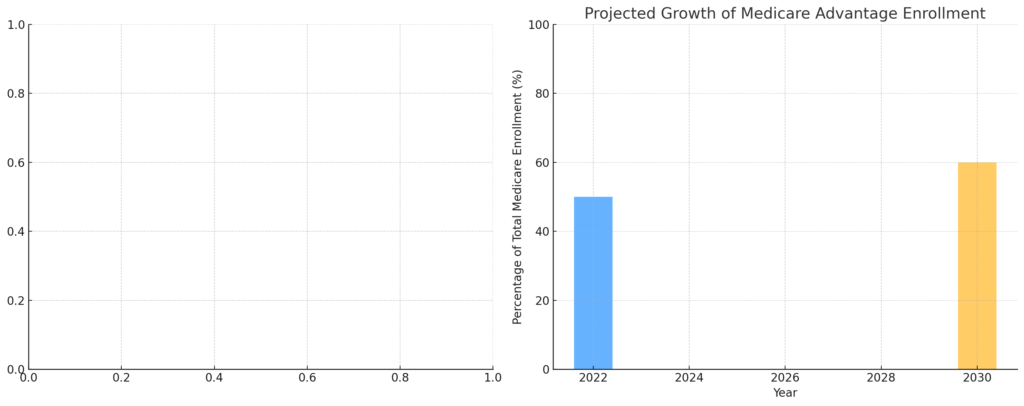
- As of January 2023, 50.5% of eligible Medicare beneficiaries are enrolled in Medicare Advantage plans.
- This signifies a notable shift from 25% in 2010 to 47% in 2021.
- Source
!Medicare vs Medicare Advantage Enrollment Over Time
Medicare Advantage: The New Frontier
Medicare Advantage plans have emerged as a new vanguard in the landscape of healthcare, offering a compelling blend of flexibility, cost-effectiveness, and enhanced benefits. As these plans gain traction, they’re reshaping how beneficiaries perceive and engage with the Medicare program.
Growth:
- In the span of just four years, from 2019 to 2023, Medicare Advantage enrollment expanded by 2.1%.
- This momentum doesn’t seem to be slowing down. Between 2022 and 2023, the program witnessed an influx of 2.3 million beneficiaries, marking a growth rate of 8%.
- Source
Popularity:
- 2023 marked a notable milestone for the program, with a record 2.7 million beneficiaries placing their trust in Medicare Advantage.
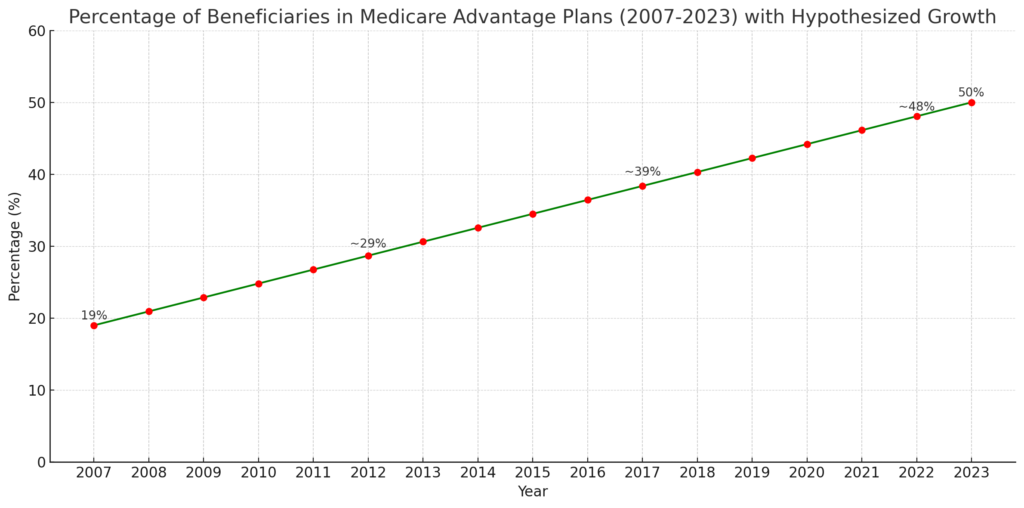
- The program’s ascendancy becomes even more evident when viewed from a long-term lens. Over a span of 16 years, from 2007 to 2023, the percentage of Medicare beneficiaries enrolled in MA plans saw a dramatic rise from 19% to a staggering 50%.

2. Economic Aspects
- At first glance, MA plans might appear more economical. Many of these plans come with low or even zero monthly premiums.
- The economic allure doesn’t stop at premiums. In 2023, MA plans have capped their out-of-pocket expenses at $8,700, offering beneficiaries predictability in their healthcare expenses.
- However, a deeper dive reveals that, on average, the federal spending per person in Medicare Advantage exceeded that for traditional Medicare beneficiaries in 2021 by a margin of 4 to 10 percent.
- Source
3. Challenges with Medicare Advantage
- The MA plans, despite their benefits, come with certain limitations. One of the primary concerns is the more restricted provider networks, potentially limiting beneficiaries’ choice of healthcare providers.
- Traditional Medicare often provides better access to high-tier hospitals and nursing homes, a luxury not always available with MA plans.
- Some beneficiaries have also raised concerns about MA plans denying benefits for certain types of care deemed not medically necessary.
- Source
Medicare’s Financial Landscape
Understanding the finances behind Medicare is crucial for insights into its sustainability, its impact on the federal budget, and potential future trajectories.
Historical Spending:
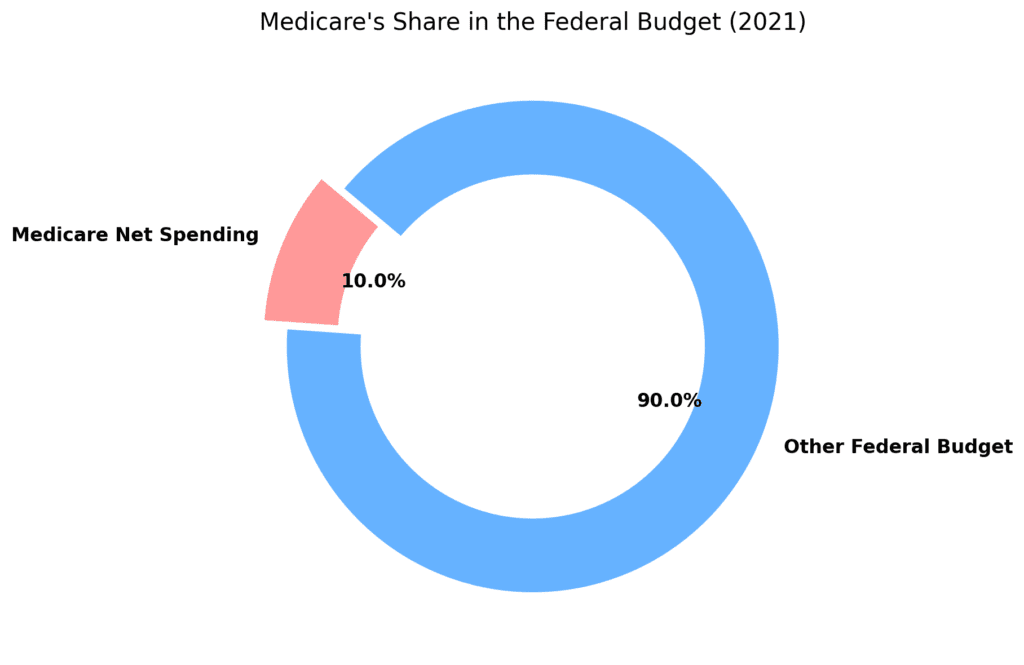
- In 2021, Medicare’s net spending amounted to $689 billion, making up 10% of the federal budget.
- Per enrollee spending surged by 6.6% in 2021.
- Medicare has consistently been a significant part of the federal budget, standing as the second-largest program last year, right after Social Security.
- Source
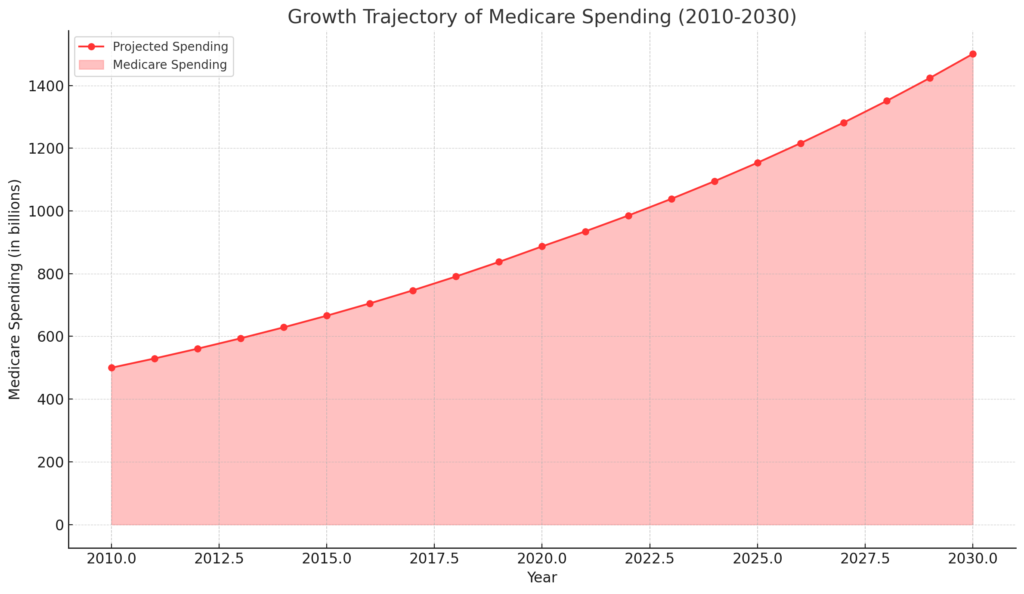
Projected Spending:
- Analysis of spending trends indicates an upward trajectory.
- Spending is projected to rise from 3.0% of GDP in 2022 to 5.5% by 2050.
- These projections emphasize the growing role of Medicare in the U.S. economy and its potential implications for future federal budgets.
- Source
Delving into Medicare Part D
Medicare Part D, the prescription drug benefit section of Medicare, serves as a vital lifeline for beneficiaries, helping them access the medications they require. Its financial and enrollment landscape, however, has seen significant shifts over time, influenced by policy changes, drug costs, and the evolving needs of the public. Here’s a detailed examination:
Enrollment and Coverage:
- As of 2022, Medicare Part D boasted a robust coverage, catering to 49 million beneficiaries.
- On the financial side, the average monthly premium stood at $33.06 in 2021, while beneficiaries encountered an average annual deductible of $445.
- The program also features a coverage gap, often termed the “Donut Hole.” In 2021, this gap initiated when a beneficiary’s total drug costs reached $4,430 and concluded once out-of-pocket expenses hit $7,050. Beyond this threshold, beneficiaries transitioned to catastrophic coverage, set at $6,550 for the year 2021.
Impact of High-Cost Drugs:
- The top 10 prescription drugs under Medicare Part D made a significant dent in the program’s financial landscape in 2021, accounting for an impressive 22% ($48 billion) of the total gross Medicare Part D drug spending.
- This stark statistic underscores the pronounced influence of high-cost drugs on the program’s overall expenditures.
Insights from Medicare Part D by Drug Dataset:
- The Medicare Part D by Drug dataset stands as a valuable repository of information, shedding light on drug-related expenditures for beneficiaries enrolled in Part D. This dataset encompasses prescriptions from physicians and other healthcare providers.
- Its contents include comprehensive details such as the number of prescriptions, beneficiaries served, and the total drug spending. This data is categorized by drug name and National Drug Code (NDC).
- Financial Landscape and Projections:
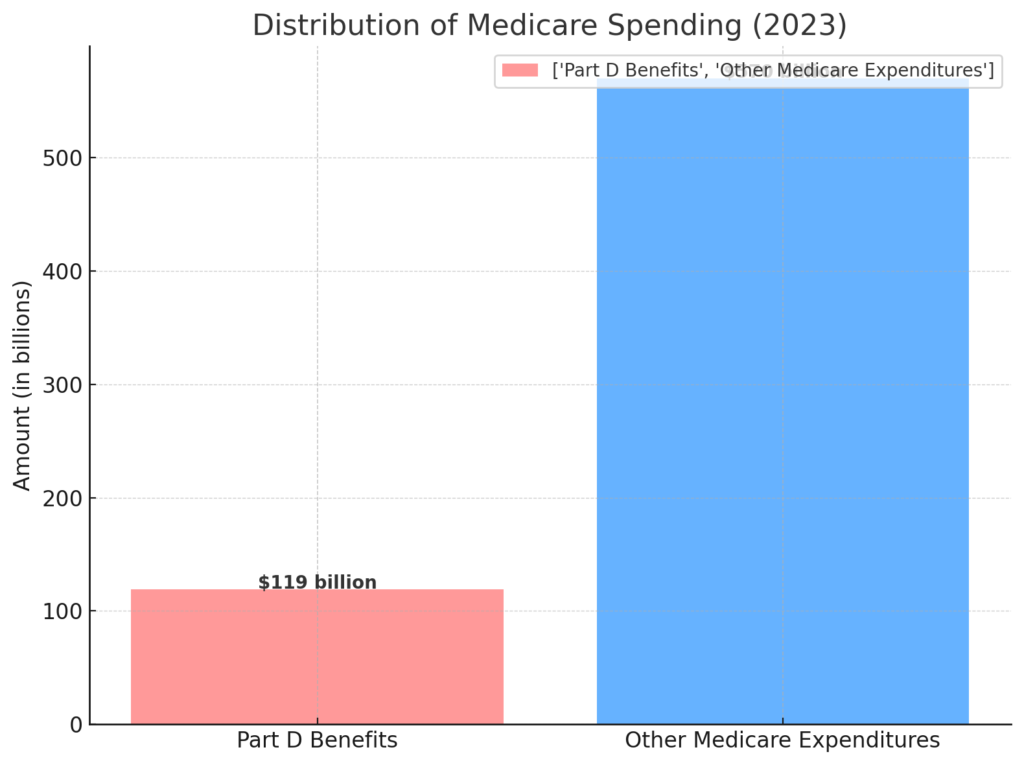
- The Congressional Budget Office (CBO) estimates that the expenditure on Medicare Part D benefits is projected to reach $119 billion in 2023. This represents approximately 14% of net Medicare spending.
- The funding for Part D originates from a tripartite arrangement: general revenues (74%), beneficiary premiums (15%), and state contributions (11%).
- Monthly premiums paid by enrollees are strategically designed to cover 25.5% of the standard drug coverage cost. The remaining 74.5% is subsidized by Medicare, based on plans’ submitted bids, which reflect their expected benefit payments.
- Source
- Historical Evolution:
- Since its inception in 2006, Medicare Part D has traversed its journey with relatively minimal alterations. Despite this consistency, the program has witnessed substantial growth in spending on the prescription drug benefit, ballooning from $44.3 billion in 2006 to $102.3 billion in 2019.
- This growth trajectory underscores the evolving landscape of prescription drug coverage within Medicare.
- Source
As Medicare Part D navigates the intricacies of high-cost drugs, financial sustainability, and evolving beneficiary needs, its role in ensuring accessible and affordable prescription medications remains essential.
Medicare Coverage Deep Dive
Medicare’s coverage extends beyond a generic scope, catering to specific illnesses, treatments, and beneficiaries’ unique needs. A closer examination of its coverage landscape reveals a nuanced approach to healthcare access.
Specific Illnesses & Treatments:
Medicare’s coverage spans a wide array of specific illnesses and treatments, ensuring beneficiaries have access to essential care when they need it most. Noteworthy areas of coverage include:
- COVID-19: Medicare plays a pivotal role in covering tests, treatments, and vaccines related to COVID-19. Beneficiaries can avail themselves of diagnostic tests, monoclonal antibody treatments, and vaccines without incurring additional costs. The comprehensive coverage aids in safeguarding public health.
- Hepatitis C: Beneficiaries grappling with Hepatitis C can find solace in Medicare’s coverage for essential treatments. Access to antiviral medications and other therapies is paramount, ensuring beneficiaries have access to appropriate care to manage and combat this condition.
Dual Eligibility:
Certain individuals navigate the complex landscape of eligibility for both Medicare and Medicaid. This dual eligibility opens avenues for comprehensive coverage, catering to a diverse range of healthcare needs.
- Eligibility Criteria: Dual eligibility extends to individuals who meet the criteria for both Medicare and Medicaid. This includes specific financial thresholds and other qualifying conditions that warrant access to both programs.
- Comprehensive Coverage: Dual eligibility bridges the gap between Medicare and Medicaid, offering beneficiaries a comprehensive coverage framework. This encompassing approach ensures that beneficiaries can access the care they need without undue financial strain.
By delving into the specifics of illnesses, treatments, and dual eligibility, Medicare underscores its commitment to delivering accessible and effective healthcare solutions for a diverse population.
Public Perception and Knowledge
Public perception and awareness play a crucial role in understanding how Medicare is perceived by the general population.
- Survey Insights on Public Awareness:
- Surveys conducted by reputable institutions often gauge the public’s understanding of Medicare, including its coverage, benefits, and enrollment process.
- These surveys may reveal how well the public comprehends the various Medicare programs and their associated costs.
- Insights into public awareness can help identify areas where education and outreach efforts are needed to ensure beneficiaries make informed choices.
- Common Misconceptions and Knowledge Deficits:
- Public misconceptions about Medicare can lead to misunderstandings and potentially impact healthcare decisions.
- Misconceptions might include confusion between Medicare and Medicaid, lack of understanding about specific coverage options, and uncertainty about eligibility criteria.
- Addressing these misconceptions through targeted communication and education campaigns can empower beneficiaries to make better-informed decisions.
Exploring the Unfolding Tale of Medicare’s Past: A Historical Perspective
- Inauguration and Evolution:
- In 1965, Medicare was established as a federal health insurance program for individuals aged 65 and above, as well as those with disabilities.
- Over the years, Medicare evolved to encompass various parts, including Part A, Part B, Part C (Medicare Advantage), and Part D (Prescription Drug Coverage).
- Landmarks Carved in Time:
- In 1997, the introduction of Medicare Advantage marked a significant milestone, offering personalized care options for beneficiaries.
- The year 2006 witnessed the inception of Part D, providing beneficiaries with vital prescription drug coverage.
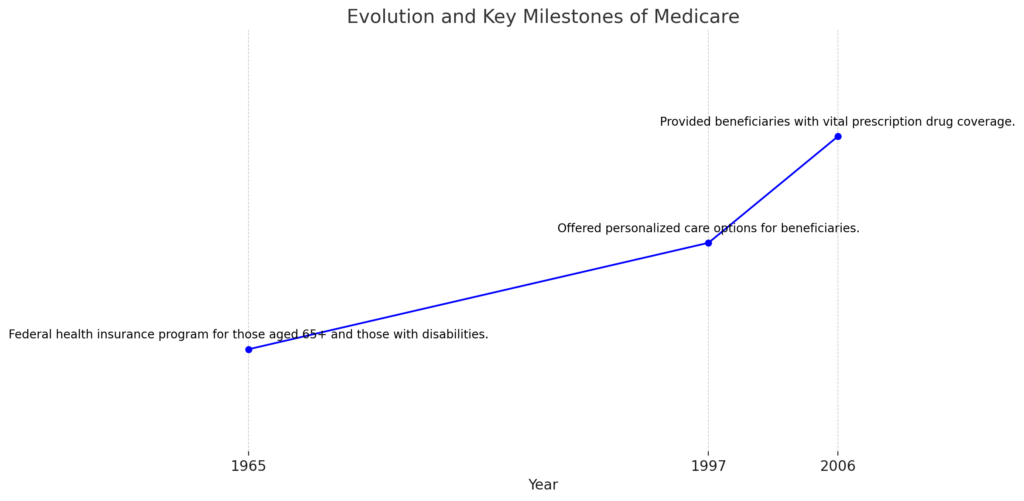
- Patterns of Enrollment: Shifting Preferences:
- Enrollment trends showcase dynamic shifts in beneficiary preferences between traditional Medicare and the allure of Medicare Advantage.
- As of 2023, a record 2.7 million beneficiaries have opted for Medicare Advantage, with the share of beneficiaries in MA plans surging from 19% to 50% between 2007 and 2023.
- Tracing the Fiscal Footprints:
- Medicare’s fiscal significance is evident through its share in the federal budget and its growth trajectory over time.
- In 2021, Medicare’s net spending amounted to $689 billion, comprising 10% of the federal budget.
- The Congressional Budget Office (CBO) estimates that spending on Part D benefits will total $119 billion in 2023, representing 14% of net Medicare spending.
- Embracing the Aging Canvas:
- The aging American population presents challenges and opportunities for Medicare, necessitating adaptation to evolving healthcare needs and medical advancements.
While specific historical data may be obscured, this journey through time highlights Medicare’s historical evolution, marked by milestones, trends, and shifts. Historical analysis serves as a compass for informed decisions, anticipates challenges, and shapes the future of Medicare as a vital pillar of healthcare for generations to come.
Peering into the Future
As we peer into the horizon, Medicare’s journey forward is illuminated by insightful predictions and statistics that provide a glimpse into its evolution, challenges, and contributions to the U.S. healthcare landscape.
- A Beacon of Healthcare Systems:
- Medicare’s trajectory is intertwined with the success of the U.S. healthcare system, positioning it as a model for health systems around the world.
- Source
- Embracing the Health Marketplace:
- Medicare’s role is poised for collaboration and integration within the existing health marketplace, rather than displacement. It will continue to coexist and “buy into” the broader healthcare ecosystem.
- Source
- Shaping the Dominant Delivery System:
- Navigating Financial Waters:
- An impending challenge emerges as Medicare may face limitations in fully covering inpatient hospital visits and nursing home stays by the year 2031.
- Social Security’s financial sustainability also raises concerns, potentially impacting benefit payouts for retirees by 2033.
- Source
- Projected Spending and Sustainability:
- Medicare’s financial footprint is projected to expand alongside its enduring role in healthcare. By 2035, total Medicare spending is estimated to rise to 8% of GDP, with further growth to 15% by 2080.
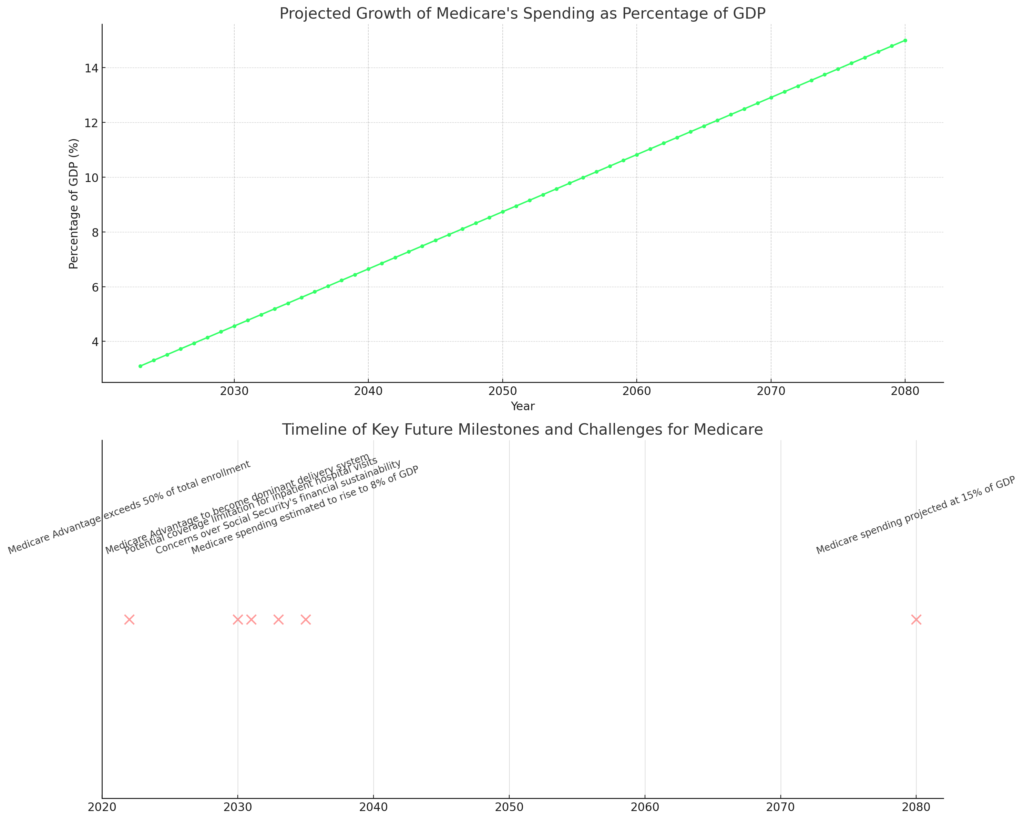
These predictions and statistics collectively underscore Medicare’s pivotal role in the U.S. healthcare ecosystem. They also highlight the imperative of addressing funding and sustainability challenges to ensure its steadfast ability to provide comprehensive coverage to beneficiaries in the years to come.
Conclusion
As we conclude our journey through the intricate landscape of Medicare, we find ourselves at a crossroads of data-driven insights and forward-looking speculations. The 2023 Medicare status indicators have illuminated the intricate web of reimbursement designations, offering clarity in a complex reimbursement ecosystem. With major, minor, and bypass indicators shaping the reimbursement landscape, healthcare providers and beneficiaries alike can navigate the reimbursement process with greater understanding.
The rise of Medicare Advantage has emerged as a defining trend, with its popularity and growth shaping the healthcare choices of millions. The economic aspects of Medicare Advantage, including cost comparisons and value assessments, present a dynamic narrative of healthcare choices and potential advantages.
Delving into Medicare Part D has unveiled the program’s impact on high-cost drugs and beneficiary experiences. From negotiations on drug prices to the top 10 prescription drugs’ financial significance, the Part D landscape is a reflection of evolving healthcare dynamics.
We’ve journeyed through historical perspectives, Medicare enrollment trends, coverage specifics, and even glimpsed into the future. Projections regarding Medicare’s growth, spending, and challenges underscore the importance of strategic planning to ensure continued comprehensive coverage for beneficiaries.
As we step back and reflect, it’s clear that Medicare’s role is intertwined with the fabric of healthcare in the United States. From its inception in 1965 to its current status as a cornerstone of healthcare coverage, Medicare continues to evolve. While challenges lie ahead, policymakers, providers, and beneficiaries must collaborate to ensure the program’s sustainability and efficacy.
Our exploration has been a mere glimpse into the vast expanse of Medicare’s intricate landscape. From its status indicators to its future trajectory, one thing remains certain: Medicare’s significance will persist as a vital pillar of healthcare access and coverage for generations to come.
References
These references provide the foundation for the insights and information presented in this comprehensive exploration of Medicare’s landscape.
Pearl Health. “6 Predictions for the Future of Medicare”
Feder, Jody, and Jonathan Gruber. “What Do Consumers Value in Health Insurance? Evidence from a Choice Experiment.” National Bureau of Economic Research.
Neuman, Tricia, and Gretchen Jacobson. “Medicare Advantage in 2022: Enrollment Update and Key Trends.” Health Affairs.
Mehrotra, Ateev, and Mary Beth Landrum. “The Future of Medicare Advantage—The Centaur of American Health Care.” JAMA Health Forum.
PBS NewsHour. “Medicare, Social Security could fall short over next decade, report says”
Congressional Budget Office (CBO). “The 2021 Long-Term Budget Outlook.”
Kaiser Family Foundation (KFF). “10 Prescription Drugs Accounted for $48 Billion in Medicare Part D Spending in 2021, or More Than One-Fifth of Part D Spending That Year.”
Medicare Interactive. “Medicare Part D Costs.”
Kaiser Family Foundation (KFF). “An Overview of the Medicare Part D Prescription Drug Benefit.”
Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS). “Medicare-Medicaid Spending by Drug.”
Commonwealth Fund. “Medicare Part D Redesign.”
Medicare.gov. “Medicare Coronavirus Coverage.”
Medicare.gov. “Hepatitis C Screening & Vaccine.”
Medicare.gov. “Dual Eligible Beneficiaries.”

